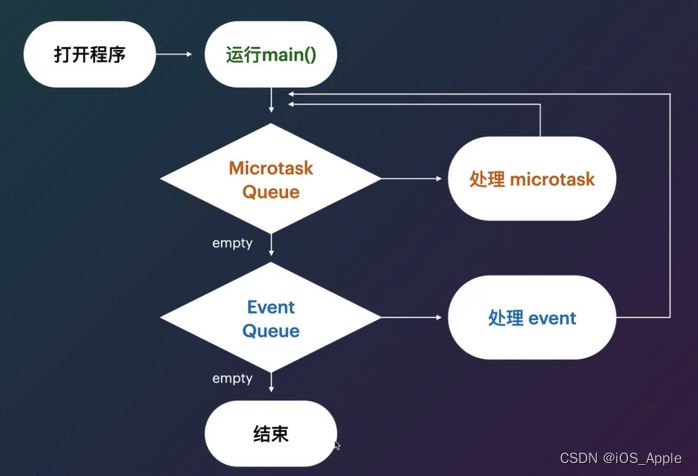
一 事件循环
flutter 就是运行在一个root isolate 中
程序只要运行起来,就有一个事件循环一直在运行 ,直至程序退出。
EventLoop 先从mrcro 对列中取任务,取完任务再去 event 队列中取任务。队列任务是FIFO。
二 认识Future
abstract class Future<T>
Future 是Dart 中提供的一个抽象类,泛型类,它用于封装一段在将来会被执行的代码逻辑。
Future就是异步中非常重要的角色。Future表示异步返回的结果,当执行一个异步延迟的计算时候,首先会返回一个Future结果,后续代码可以继续执行不会阻塞主isolate,当Future中的计算结果到达时,如果注册了 then 函数回调,对于返回成功的回调就会拿到最终计算的值,对于返回失败的回调就会拿到一个异常信息
1 基本使用
Flutter提供了下面三个方法,让我们来注册回调,来监听处理Future的结果。
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
//处理完成时候的回调,一般都是成功回调Future<R> then<R>(FutureOr<R> onValue(T value), {Function onError});//处理失败的回调,比如throw一个error就会走到这里Future<T> catchError(Function onError, {bool test(Object error)});//Future.whenComplete总是在Future完成后调用,不管Future的结果是正确的还是错误的。Future<T> whenComplete(FutureOr action()); |
代码示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 |
import 'dart:io'; main(List<String> args) { // 阻塞主线程的调用 // blockMainThread(); // 异步调用 asyncMethod();} /*****----- 异步的调用方式 ---***/void asyncMethod() { /** * main start main end hello world * */ print("main start"); var future = getAsyncNetworkData(); future.then((String value) { // 只有拿到结果 才会执行这里面的代码 print(value); }).catchError((error) { // 打印结果 Exception: 我是错误信息 print(error); }).whenComplete(() { // 代码走这,不管成功或者失败都会走这里 print("代码执行完毕"); }); print("main end");} Future<String> getAsyncNetworkData() { return Future<String>(() { sleep(Duration(seconds: 3)); // return "hello world"; // 抛出异常 throw Exception("我是错误信息"); });} /*****----- 阻塞主线程的调用方式 ---***/void blockMainThread() { /** * main start this is hello world main end * */ print("main start"); var res = getNetworkData(); print(res); print("main end");} // 模拟网络请求String getNetworkData() { // 阻塞2秒 sleep(Duration(seconds: 2)); return "this is hello world";} |
2 链式调用
链式调用优势在于可以明确代码执行前后依赖关系以及实现异常的捕获
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 |
import 'dart:io'; main(List<String> args) { print("main start"); /** * main start main end 第一次网络请求的结果 第二次网路请求的结果 第三次网路请求的结果 * * */ // 这种方式可以解决回调地狱的问题 多个网络请求依赖也不用进行嵌套调用 直接链式调用即可 Future(() { // 这是第一次网络请求 sleep(Duration(seconds: 2)); return "第一次网络请求的结果"; }) .then((res) { print(res); sleep(Duration(seconds: 2)); // 这是第二次网络请求 return "第二次网路请求的结果"; }) .then((res) { print(res); sleep(Duration(seconds: 2)); return "第三次网路请求的结果"; }) .then((value) => print(value)) .catchError((error) { print(error); }); print("main end");} |
三 await 和 async
要定义异步函数,请在函数主体之前添加async关键字,他俩是配对出现的
他们是dart 语言中的关键字,最为重要的使用就是
可以让我们用同步的代码格式去实现异步的调用过程。
大部分Future使用的场景都可以使用async-await来替代,也建议使用async-await。
下面有这样一个需求 :比如说用户登录完成之后,拿到用户的token 去请求数据,就是请求之间的依赖
用 await async 方式实现 和 Future 实现比较
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 |
import 'dart:io'; main(List<String> args) { print("main start"); // getData(); futureMethodData(); print("main end");} // future 的实现方式futureMethodData() { Future(() { // 这是第一次网络请求 sleep(Duration(seconds: 2)); return "这是第一次网络请求结果"; }).then((value) { print(value); sleep(Duration(seconds: 2)); return value + "这是第二次网络请求结果"; }).then((value) { print(value); sleep(Duration(seconds: 2)); return value + "这是第三次网络请求结果"; }).then((value) { print(value); });} // async-await 的实现方式getData() async { // 模拟三次网络请求 /** * * main start main end args1helloworld args1helloworldhelloworld args1helloworldhelloworldhelloworld */ var res1 = await getNetworkData("args1"); print(res1); var res2 = await getNetworkData(res1); print(res2); var res3 = await getNetworkData(res2); print(res3);} getNetworkData(String args) { return Future(() { sleep(Duration(seconds: 2)); return args + "helloworld"; });} |
四 isolate
isolate 可以理解为dart 中的多线程,现在设备基本都是多核CPU,可以使用isolate 充分利用硬件资源。
isolate 之间是独立的,资源不共享的。每一个isaolate 都有自己的事件循环以及队列。
1 使用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 |
import 'dart:io';import 'dart:isolate'; main(List<String> args) async { print("main start"); // 1 ReceivePort receivePort = ReceivePort(); // 2 spawn 返回的是future 所以要异步操作 Isolate isolate = await Isolate.spawn<SendPort>(calculate, receivePort.sendPort); // 可以给创建的isolate 中发送消息 receivePort.sendPort.send("这是从main isolate 发送的消息"); //3 监听创建的isolate的回调信息 receivePort.listen((message) { print(message); // 收到结果 关闭 kill receivePort.close(); isolate.kill(); }); print("main end");} calculate(SendPort port) { // 模拟耗时操作 sleep(Duration(seconds: 2)); // 回调信息 port.send("这是从创建的isolate 发送的信息");} |